Results of the analysis of the RAX-1 and RAX-2 attitude determination system have recently been published.
John C. Springmann, James W. Cutler, Flight results of a low-cost attitude determination system, Acta Astronautica, Volume 99, June–July 2014, Pages 201-214, ISSN 0094-5765, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.actaastro.2014.02.026.
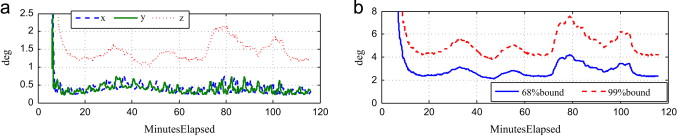
The paper presents flight results of the attitude determination system (ADS) flown on the Radio Aurora Explorer (RAX) satellites, RAX-1 and RAX-2, which are CubeSats developed to study space weather. The ADS sensors include commercial-off-the-shelf magnetometers, coarse sun sensors (photodiodes), and a MEMs rate gyroscope. A multiplicative extended Kalman filter is used for attitude estimation. On-orbit calibration was developed and applied to compensate for sensor and alignment errors, and attitude determination accuracies of 0.5° 1–σ have been demonstrated on-orbit. The approach of using low-cost sensors in conjunction with on-orbit calibration, which mitigates the need for pre-flight calibration and high-tolerance alignment during spacecraft assembly, reduces the time and cost associated with the subsystem development, and provides a low-cost solution for modest attitude determination requirements. Although the flight results presented in this paper are from a specific mission, the methods used and lessons learned can be used to maximize the performance of the ADS of any vehicle while minimizing the pre-flight calibration and alignment requirements.